Home » Global Perspective of Biodiversity, Climate Change and Food Security
Human activity as much as natural elements are to blame for climate change (CC). Biodiversity, agricultural output, and food security are all expressively altered. The majority of endemic and narrowly adapted species are in danger of extinction. Concerns regarding the extinction of species are merited because they provide sustenance for all life forms and primary health care for more than 60–80 % of humans worldwide. Despite the fact that the impact of climate change on biodiversity and agricultural security has been acknowledged, relatively little is known about the global scope of the problem. Moreover, climate change has an impact on food security, especially in communities and regions that rely on rain-fed agriculture. Plants and crops have limits beyond which their growth and yield are compromised. In reaction to a changing future climate globally, it is expected that biodiversity, agricultural productivity, and food security would change significantly. Therefore, one of the anticipated effects of CC is the transfer of plants from the environment to which they are acclimated to higher altitudes and latitudes.
Intensively managed ecosystems (agriculture, plantation forestry, and aquaculture) and non-intensively managed ecosystems (pasture lands, native forests, freshwater ecosystems, and oceans) support biodiversity. In addition to solar radiation, carbon dioxide level, ambient temperature, and the availability of water and inorganic nutrients, the existence of life is primarily dependent on the evaporative capacity of the atmosphere. However, these crucial parameters, upon which life depends, are affected by both natural and human-caused factors. Consequently, the swiftly expanding human population and economies over the past century have increased the demand for biodiversity resources.
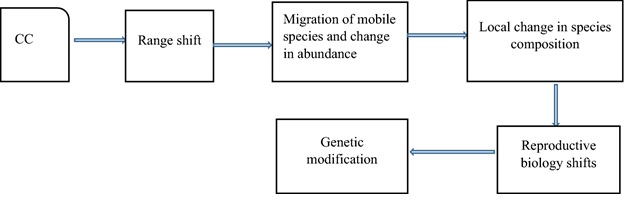
Methods for keeping species alive in a changing climate
Food, novel medications, and genetic variety that may have evolutionary significance for pest resistance, soil fertility, and pollination are all unavoidable benefits of biodiversity. Consequently, the provision of biodiversity services is necessary for food production. Such strategies can rely on an expanded agricultural base combined with various habitats.
Therefore, ensuring food security in the face of a changing climate and the loss of biodiversity is difficult to do absent reforms in policy, land use, and investment. Applying CC mitigation policy measures, reducing food waste, and reversing land degradation might all have a good impact. One of the main adaptation and mitigation measures for the worldwide effects of CC is the re-discovery and release of high-yielding, biotic and abiotic stress resistant and appropriate varieties across agro-ecologies.
Dr. Swapnila Roy
HOD, SOBAS
August 28, 2023
RECENT POSTS
CATEGORIES
TAGS
Agriculture Agriculture future AI Architecture artificial intelligence Bachelor of Commerce BA English BA Psychology BTech AIML BTech CSE BTech cybersecurity BTech Engineering Business management career Career-Specific Education career guide career option career scope Civil engineering commerce and management Computer Science Computer science engineering Data science degree education Engineering Engineering students English Literature english program Fashion Design Fashion design course Higher Education Journalism journalism and mass communication law Law career Machine Learning mathematics MBA MBA specialization Mechanical Engineering Pharmacy Psychology Research and Development students
Lingaya's Vidyapeeth (LV) only conducts physical/online verification of any document related to examination on the following official email IDs:
It is important to note that the following email IDs and domains are fraudulent and do not belong to our university:
Please do not respond to or share any personal information with these fraudulent sources.